Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology
What is biological science?

Biology is the report of life. The discussion "biology" is derived from the Greek words "bios" (pregnant life) and "logos" (meaning "study"). In full general, biologists study the structure, role, growth, origin, development and distribution of living organisms.
Biology is important because information technology helps the states understand how living things work and how they function and interact on multiple levels, according to the Encyclopedia Britannica. Advances in biological science have helped scientists practise things such as develop meliorate medicines and treatments for diseases, understand how a irresolute environment might affect plants and animals, produce plenty food for a growing man population and predict how eating new food or sticking to an exercise regimen might affect our bodies.
The bones principles of modern biology
Iv principles unify modern biology, according to the book "Managing Science" (Springer New York, 2010):
- Jail cell theory is the principle that all living things are fabricated of fundamental units called cells, and all cells come from preexisting cells.
- Gene theory is the principle that all living things have Deoxyribonucleic acid, molecules that code the structures and functions of cells and get passed to offspring.
- Homeostasis is the principle that all living things maintain a land of residue that enables organisms to survive in their surroundings.
- Development is the principle that describes how all living things can alter to have traits that enable them to survive better in their environments. These traits result from random mutations in the organism's genes that are "selected" via a procedure called natural choice. During natural selection, organisms that have traits meliorate-suited for their environs have higher rates of survival, and then pass those traits to their offspring.
The many branches of biology
Although there are only four unifying principles, biological science covers a broad range of topics that are broken into many disciplines and subdisciplines.
On a loftier level, the different fields of biology can each be thought of as the study of one blazon of organism, according to "Blackie's Dictionary of Biology" (S Chand, 2014). For example, zoology is the study of animals, botany is the study of plants and microbiology is the study of microorganisms.
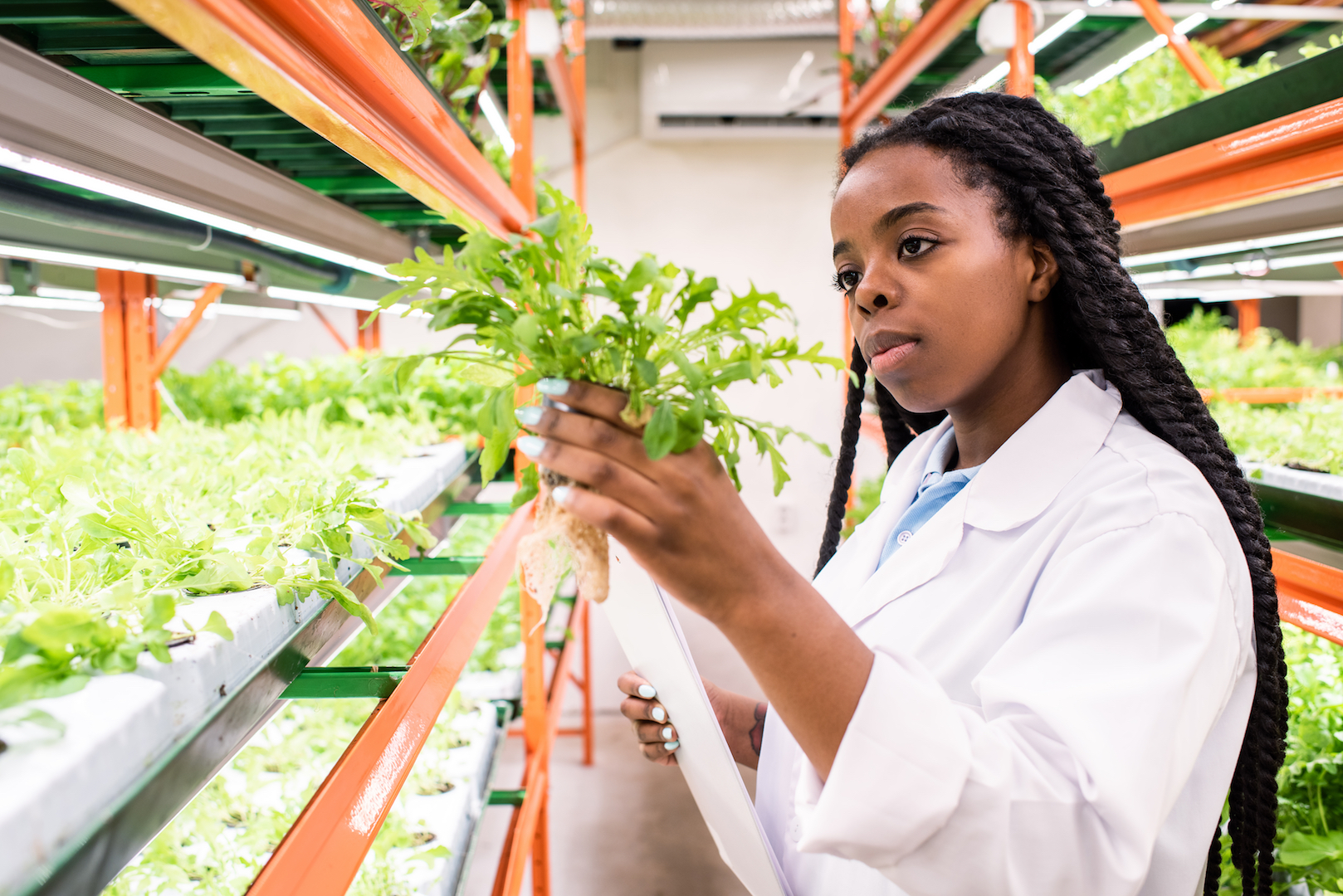

Within those broader fields, many biologists specialize in researching a specific topic or problem. For example, a scientist may study behavior of a certain fish species, while another scientist may inquiry the neurological and chemical mechanisms behind the behavior.
At that place are numerous branches and subdisciplines of biology, but hither is a brusk listing of some of the more broad fields that autumn under the umbrella of biology:
Biochemistry: The study of the chemical processes that take identify in or are related to living things, according to the Biochemical Society. For instance, pharmacology is a type of biochemistry research that focuses on studying how drugs interact with chemicals in the body, as described in a 2010 review in the periodical Biochemistry.
Ecology: The written report of how organisms interact with their environment. For example, an ecologist may study how honeybee behavior is affected by humans living nearby.
Genetics: The report of heredity. Geneticists study how genes are passed downward by parents to their offspring, and how they vary from person to person. For example, scientists have identified several genes and genetic mutations that influence human lifespan, as reported in a 2019 review published in the journal Nature Reviews Genetics.
Physiology: The report of how living things work. Physiology, which is applicative to whatsoever living organism, "deals with the life-supporting functions and processes of living organisms or their parts," according to Nature. Physiologists seek to understand biological processes, such as how a particular organ works, what its function is and how it'due south affected by exterior stimuli. For example, physiologists have studied how listening to music can cause physical changes in the homo body, such as a slower or faster heart rate, according to the periodical Psychological Health Effects of Musical Experiences. .
The multidisciplinary nature of biological science
Biology is frequently researched in conjunction with other fields of study, including mathematics, engineering and the social sciences. Hither are a few examples:
Astrobiology is the written report of the development of life in the universe, including the search for extraterrestrial life, co-ordinate to NASA. This field incorporates principles of biology with astronomy.
Bioarchaeologists are biologists who contain archaeological techniques to study skeletal remains and derive insights most how people lived in the past, according to George Stonemason University.
Bioengineering is the application of engineering science principles to biological science and vice versa, according to the University of California Berkeley. For case, a bioengineer might develop a new medical technology that better images the inside of the body, similar an improved Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) that scans the homo body at a faster charge per unit and higher resolution, or utilize biological knowledge to create artificial organs, according to the periodical Jail cell Transplant.
Biotechnology involves using biological systems to develop products, according to the Norwegian Academy of Science and Technology. For example, biotechnologists in Russia genetically engineered a improve-tasting and more disease-resistant strawberry, which the researchers described in their 2007 study published in the journal Biotechnology and Sustainable Agriculture 2006 and Beyond.
Biophysics employs the principles of physics to empathize how biological systems piece of work, according to the Biophysical Society. For example, biophysicists may written report how genetic mutations leading to changes in poly peptide structure impacts protein evolution, according to the Journal of the Royal Society
What practice biologists do?
Biologists can work in many different fields, including research, healthcare, ecology conservation and art, according to the American Institute of Biological Sciences. Here are a few examples:
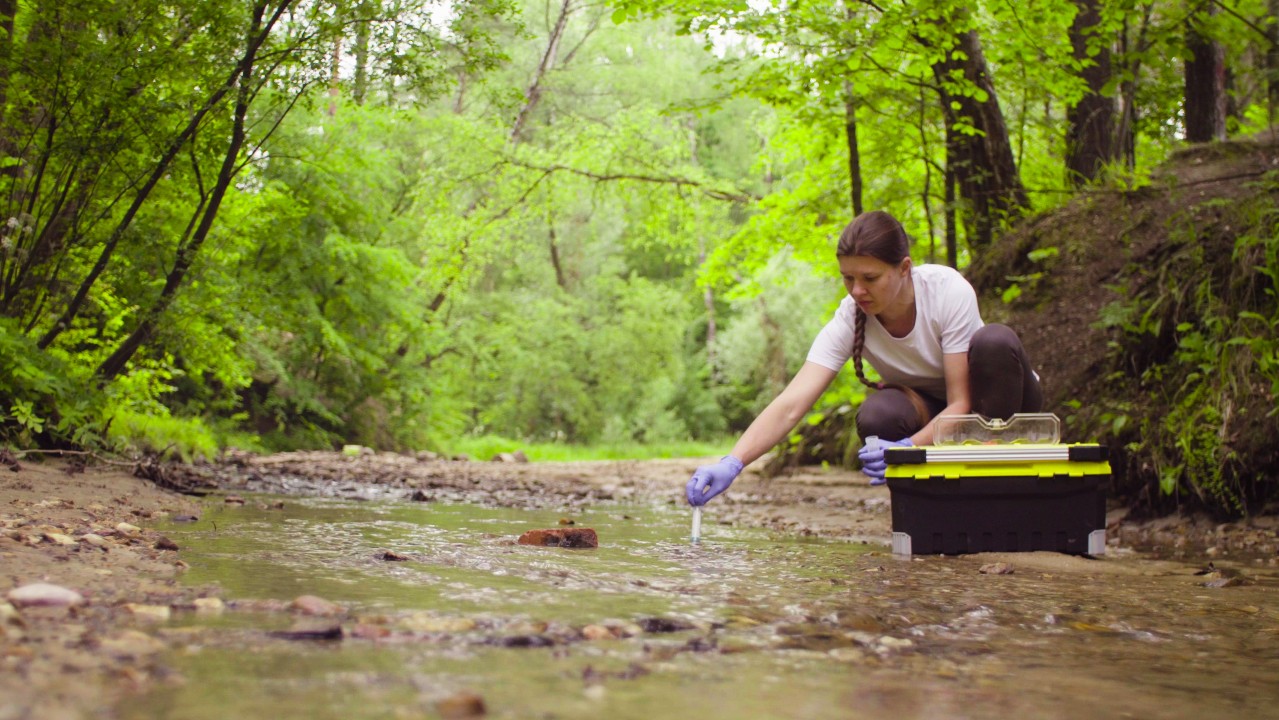
Inquiry: Biologists tin perform enquiry in many types of settings. Microbiologists, for instance, may study bacterial cultures in a laboratory setting. Other biologists may perform field research, where they observe animals or plants in their native habitat. Many biologists may work in the lab and in the field — for example, scientists may collect soil or water samples from the field and analyze them further in the lab, like at North Carolina University's Soil and Water Lab.
Conservation: Biologists can assistance with efforts in environmental conservation by studying and determining how to protect and conserve the natural world for the hereafter. For instance, biologists may help educate the public on the importance of preserving an beast's natural habitat and participate in endangered species recovery programs to terminate the pass up of an endangered species, co-ordinate to the U.S. Fish & Wild animals Service.

Healthcare: People who written report biology tin can go on to work in healthcare, whether they work equally doctors or nurses, join a pharmaceutical company to develop new drugs and vaccines, inquiry the efficacy of medical treatments or become veterinarians to assistance care for sick animals, co-ordinate to the American Institute of Biological Sciences.
Art: Biologists who also accept a groundwork in fine art have both the technical knowledge and artistic skill to create visuals that will communicate circuitous biological information to a broad variety of audiences. I example of this is in medical analogy, in which an illustrator may perform background research, collaborate with experts, and observe a medical procedure to create an accurate visual of a body function, according to the Association of Medical Illustrators.
Additional resources
If you're curious about just how wide-reaching biology is, The University of North Carolina at Pembroke has listed a number of biological science subdisciplines on their website. Interested in a career in biology? Bank check out some options at the American Institute of Biological Sciences website.
Bibliography
Lornande Loss Woodruff, "History of Biology", The Scientific Monthly, Volume 12, March 1921, http://www.jstor.org/stable/6836.
P.N. Campbell, "Biological science in Profile: A Guide to the Many Branches of Biology", Elsevier, October 2013.
The Academy of N Carolina at Pembroke, "Biology Sub-disciplines", October 2010.
University of Minnesota Duluth, "What is Biology?", Jan 2022.
Eric J. Simon et al, "Campbell Essential Biology", Pearson Pedagogy, January 2018.
Source: https://www.livescience.com/44549-what-is-biology.html
0 Response to "Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology"
Post a Comment